Algorithm design is often regarded as the backbone of computer science, but for many students thousands of IGNOU BCA students, it may be the biggest mountain to climb when appearing for semester exams. If you recently sat for the exam or are preparing for the next cycle, you are likely looking for the BCS 042 Question Paper from June 2025 to understand exactly what went right or wrong. At Unnati Education, we don’t just give you questions; we dissect the logic behind every algorithm to ensure that you are not just memorising some code, but you are understanding the method.
We have analysed the latest trends regarding the exams from the June 2025 session 1. Frankly, the paper was balanced but quite technical and required a good grasp of time complexity, recursive logic, and graph theory. In this detailed guide, we will guide you through the solutions, common pitfalls, and the exact strategies required by you to score high marks in this particular subject.
For more IGNOU papers or support, you may visit: https://www.unnatieducations.com/ignou.
Crucial Resources on Algorithm Design for Students
Before jumping into the technical breakdown, it is important to assemble the proper materials. Most students begin their preparation by searching for the BCS 042 question paper to understand the exam pattern. Once you have the paper, the next step is locating a reliable BCS 042 solved question paper to verify your logic, especially for mathematical problems like recurrences. We also recommend maintaining a checklist of every Algorithm Design Important Question that has appeared frequently over the last five years. Since the BCS 042 question paper June 2025 represents the latest standard set by the university, using a comprehensive BCS 042 question paper solution based on it is the smartest strategy for your upcoming exams.
BCS 042 Question Paper June 2025 – Quick Overview
Before we get into the specific algorithms and solutions, let’s see the “vital statistics” of this exam. Understanding the structure is the first step toward mastering the BCS 042 Question Paper.
| Exam Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Course Code | BCS-042 3 |
| Course Title | Introduction to Algorithm Design 4 |
| Exam Session | June 2025 5 |
| Maximum Marks | 50 Marks 6 |
| Duration | 2 Hours 7 |
| Paper Structure | Q1 is Compulsory (20 Marks). Attempt any 3 from the rest. 8 |
| Key Topics Covered | Recursion, Greedy Method, Graphs (Dijkstra/Prim) Sorting (Bubble/Quick) |
Why Does the “BCS 042 Question Paper” Feel Difficult for Students
One of the reasons why this particular paper appears intimidating is not because of its code; it is the theoretical justification needed. In practical subjects, such as C++, Java, you write the programme and run it. However, in the BCS 042 Question Paper, you have to write the algorithm, explain the logic in English, and then mathematically calculate the time complexity (Big O notation).
The leap from “coding” to “analyzing” is a jarring one for a lot of students. You can not just memorise a program using Quick Sort, but in the average case but you need to figure out the reason why it’s faster compared to Bubble Sort and why it is slower than Bubble Sort in the worst case. The paper in June 2025 specifically tested this analytical ability, and not just for definition, but asking for step-by-step logic, as well as cases of complexity (Best, Worst, Average). On top of that, graph algorithms such as Dijkstra’s and Prim’s require a visual understanding of nodes and edges, which is tricky to put on paper, especially with the time constraint.
BCS 042 Question Paper June 2025 Sample Pages




Need BCS-042 Question Paper Solutions?
If you’re looking at these questions and wondering where to even begin, relax—we’ve got you covered.
We’ve done the hard work for you. For BCS-042, students can get full solved papers, customized assistance, detailed study notes, and expert exam tips from our dedicated team. Our focus is on helping you truly grasp the concepts, not just rote learning.
Check out our IGNOU support services here: https://www.unnatieducations.com/ignou.
BCS 042 Question Paper – See full question paper video
Sometimes, it’s not enough to read. You have to see the logic in action to really understand how recurrences or graph traversals work. We have recorded a complete and step-by-step solution for the video where we solve the paper from June 2025 live with explaining the “why” and “how” part of each step.
BCS 042 Question Paper June 2025 – Question-Wise Analysis
We have decoded specific questions from the June 2025 paper. Below, we discuss the basic idea behind each question and what the examiner was expecting you to say over the period of 1-2 lines.
Question 1:The Compulsory Section (20 Marks)
This section is more on the breadth of the syllabus, so you have to jump from one algorithm paradigm to another fast.
- 1(a) What do you mean by a recursive algorithm? [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: This is a question asking for a formal textbook definition of an algorithm (emphasize finiteness and precision) 13 as well as an explanation of recursion, in which the function makes a recursive call to itself to solve smaller sub-problems14. - 1(b) Time Complexity Linear Search [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: You are supposed to analyze the performance of a sequential search, i.e., with Best Case (element at the start) and Worst Case (element at the end) scenarios. - 1(c) Brief Notes (Backtracking, Knapsack, Graphs, Euclid) [6 Marks]
Concept Explanation: This section assesses your capacity to briefly summarize complicated topics: Backtracking as a “trial and error” search exploration, Fractional Knapsack as a Greedy optimization, Connected Graphs as an accessible path, and Euclid’s method for finding GCD. - 1(d) Greedy Approach for Currency Notes [4 Marks]
Concept Explanation: This is a very practical application of the Greedy Method, where you must show how you would choose the largest possible currency point and keep doing it until you solve the problem of finding the least number of notes for a given amount (i.e., 437).
Question 2: Recurrences, Asymptotic Analysis
- 2(a) Solving the Recurrence tree [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: To solve this mathematical question, you have to understand how the cost of an algorithm working at each level is represented in a tree structure by calculating a sum and total work done by the algorithm (T(n)=T( \lfloor n/3 \rfloor) + T(\lfloor 2n/3 \rfloor) + n) . - Questions 2(b) Asymptotic Comparison [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: This questions your understanding of the Master Theorem, you need to mathematically compare the growth rates from two different recurrence relations so as to find out which algorithm is faster 19.
Question 3: Sorting and Distance Minimized
- 3(a) Bubble Sort Analysis [5 Marks]
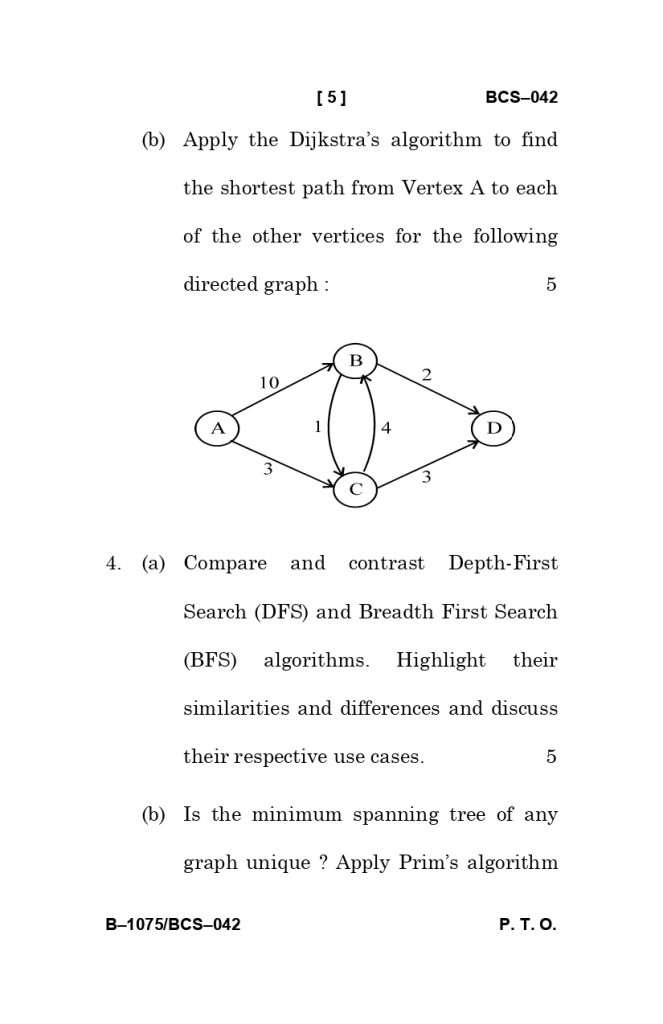
Concept Explanation: You have to write a complexity analysis of the Bubble Sort algorithm, i.e., how the time complexity changes from $O(n^2)$ to $O(n)$ when given an input array that is already sorted 20. - 3(b) Dijkstra’s Algorithm [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: Which requires ‘Single Source Shortest Path’ algorithm has to be executed on a given graph manually by increments of distance value node-wise until the destination is reached.
Question 4: Graph Traversals & MST
- 4(a) DFS vs BFS [5 Marks]
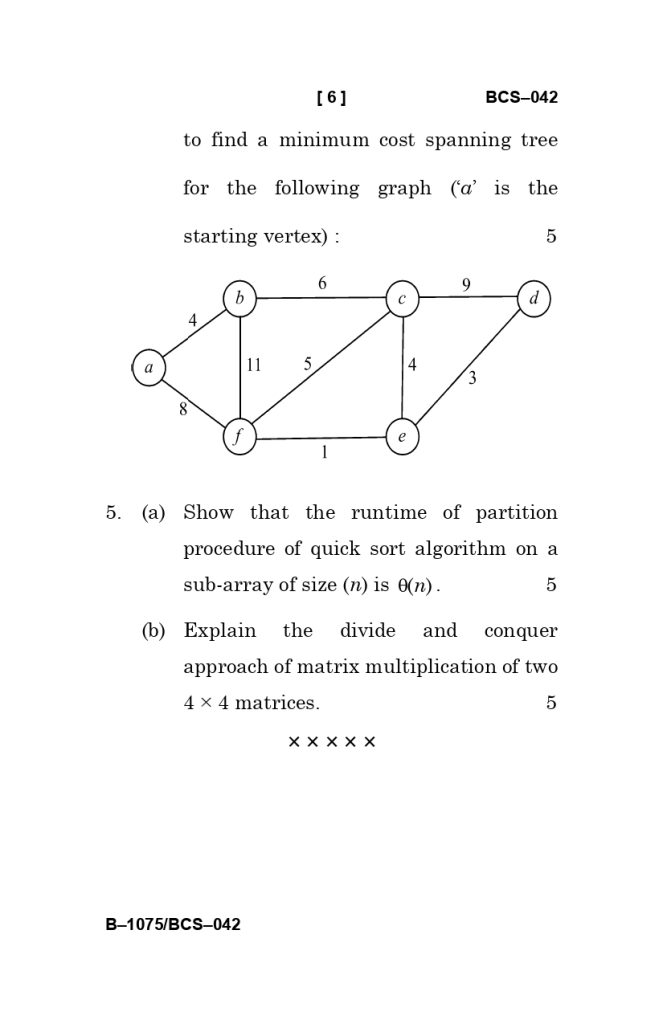
Concept Explanation: This is a theoretical something comparison, involving you to differentiate between Depth-First Search (stack-based) and Breadth-First Search (queue-based) in terms of order of traversal and applications. - 4(b) Prim’s Algorithm & Uniqueness of MST [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: You will have to deal with the theoretical situation when a Minimum Spanning Tree does not have unique solutions (distinct edge weights) and show the step-by-step construction of an MST by Prim’s method.
Question 5: QuickSort and Multiplication of Matrices
- 5(a) Analysis of Quick Sort Partition [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: We need to write a proof/logical explanation to find that the process of dividing the array around the pivot element touches each and every element exactly once =>linear time complexity. - 5(b) Divide and Conquer algorithm for Multiplication of matrices [5 Marks]
Concept Explanation: You have to explain the concept of decomposing the large matrix multiplication into smaller $4 \times 4$ sub-matrices to solve the problem recursively and make frequent references to Strassen’s approach.
Important Topics BCS 042 Based on Previous Papers
- Sorting Algorithms: Quick Sort and Merge Sort are staples. Understand the “Divide and Conquer” strategy behind them.
- Graph Theory: You must know how to manually go through the processes of running BFS, DFS, Prim’s, and Kruskal’s on a drawn graph.
- Dynamic Programming: Although this paper has mostly dealt with Greedy, under the topic of DP, topics such as Matrix Chain Multiplication frequently arise.
- Master Theorem: You will end up with a hand-written almost always will get a recurrence relation to solve. Memorizing the 3 cases of the Master Theorem is non-negotiable.
Answer Writing Strategy of Unnati Education
- Start with a Definition: Always start with a definition of the term (e.g., “What is a Spanning Tree?”).
- Use Pseudocode: Don’t write full C++ code unless you are asked. Write clear and English-like steps.
- Visuals are Key: For Graph questions, or Recursion trees – A Visual diagram is for 50% of the marks.
- Analysis Table: Always end with a small table with Time and Space complexity.
- Conclusion: In a sentence of one line, summarize your understanding. For example, “Therefore, Greedy is faster, but they don’t always provide the optimal solution for every problem.”
For more IGNOU papers or support, you may visit: https://www.unnatieducations.com/ignou.
Some Mistakes that You as a Student Should Try to Avoid
- Ignoring Base Cases: For Recursion. If you forget to write the Base cases for Recursion, then the logic is not valid, and you end up in an infinite loop.
- Confusing 0/1 with Fractional Knapsack: One uses Dynamic Programming, the other is a Greedy one. Don’t mix them up26.
- Writing Paragraphs Instead of Steps. Algorithms are step-by-step. Don’t write long essays; use lists with numbers.
- Forgetting Units: For the sake of complexity, always write O(n) or O(log n). Just writing “n” mathematically is not correct.
Time Management while Taking the Exam
- First 15 Mins: Scan the paper. Pick the 3 optional questions that you know the best.
- Next 40 Mins: This time is just dedicated to Compulsory Question 1. It is worth 40% of the total marks (20 marks). Do not rush this.
- Remaining Time: Divide this time between the remaining 3 questions (approx 20 mins each)
- Tip: If you get stuck with a mathematical proof (like Q2b), leave space and move on. Don’t waste 20 minutes on a 5 mark calculation.
Algorithm Design Cheatsheet: The “Big O” Complexity Conclusion Table
| Algorithm | Best Case | Average Case | Worst Case | Space Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Search | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Binary Search | O(1) | O(log n) | O(log n) | O(1) |
| Bubble Sort | O(n) | O(n²) | O(n²) | O(1) |
| Quick Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n²) | O(log n) |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | O(n) |
| Dijkstra | O(V²) | O(E log V) | – | O(V) |
Final Thoughts on BCS 042 Question Paper June 2025
The BCS 042 Question Paper from June 2025 serves as a perfect blueprint for future exams. It points to the importance of not merely memorizing definitions but also understanding the “how” and “why” of algorithms. By focusing on the structural breakdown we provided, i.e, Recursion, Searching, Graph Traversals, you can make this “difficult” subject your highest-scoring paper.
Prepare well, pay attention to the logic, and always keep in mind that every complicated algorithm consists of a series of simple steps that are put together. Good luck with your studies.
















