NIOS Class 12 Biology 314 TMA Solved 2025-26: Complete Guide with Question Analysis
Worried about your NIOS Class 12 Biology 314 TMA submission for the 2025-26 session and unsure how to answer the questions correctly to score maximum marks? Understanding the TMA pattern, knowing what examiners expect, and submitting on time are crucial for securing the 16 marks that directly add to your final result. This comprehensive guide analyses the actual Biology 314 Solved TMA questions, explains the answer approach for each section, and provides everything you need to submit a high-scoring assignment before the January 31, 2026, deadline.
Quick Overview: Biology 314 TMA 2025-26
| Details | Information |
|---|---|
| Subject Code | 314 (Biology/Jeev Vigyan) |
| Session | April 2025 to March 2026 |
| Total Marks | 20 (converted to 16 = 20% of total) |
| Total Questions | 6 (with internal choices in Q1, Q2, Q6) |
| Submission Mode | Online via NIOS Student Portal |
| Answer Format | Handwritten only (no typed submissions) |
| Last Date (April 2026 Exam) | January 31, 2026 |
| Last Date (October 2026 Exam) | July 31, 2026 |
| Evaluation By | Subject tutor at your study centre |
| Late Submission | Not accepted (zero marks awarded) |
| Compulsory For | All Stream-1 NIOS learners |
Understanding the TMA Structure
The NIOS Class 12 Biology TMA for 2025-26 follows a consistent pattern that tests your understanding across different topics from the Biology curriculum. Let me break down what you’re actually facing.
Question Pattern Breakdown:
The TMA contains six main questions with varying marks and word limits. Questions 1 and 2 each carry 2 marks and require short answers of 40 to 60 words. You get to choose between two options (a or b) for both these questions, which means you can pick the one you’re more confident about.
Questions 3, 4, and 5 are compulsory without any choices. Each carries 4 marks and requires detailed answers of 100 to 150 words. These questions test your comprehensive understanding of specific topics and require well-structured, complete explanations.
Question 6 is unique. It’s a project-based question worth 6 marks where you again get two options to choose from. One option typically involves practical work or field observation, while the other focuses on theoretical research or comparative analysis. This question requires the most effort but also offers a good scoring opportunity if done properly.
Marks Distribution:
| Question | Marks | Word Limit | Type | Choice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Question 1 | 2 | 40–60 words | Short Answer | Choose a or b |
| Question 2 | 2 | 40–60 words | Short Answer | Choose a or b |
| Question 3 | 4 | 100–150 words | Long Answer | Compulsory |
| Question 4 | 4 | 100–150 words | Long Answer | Compulsory |
| Question 5 | 4 | 100–150 words | Long Answer | Compulsory |
| Question 6 | 6 | Project work | Project | Choose a or b |
| Total | 20 | – | – | – |
Key Topics Covered in 2025-26 TMA
Based on the actual TMA released for this session, several important topics from your Biology syllabus are covered. Understanding these helps you prepare better.
Evolution and Natural Selection:
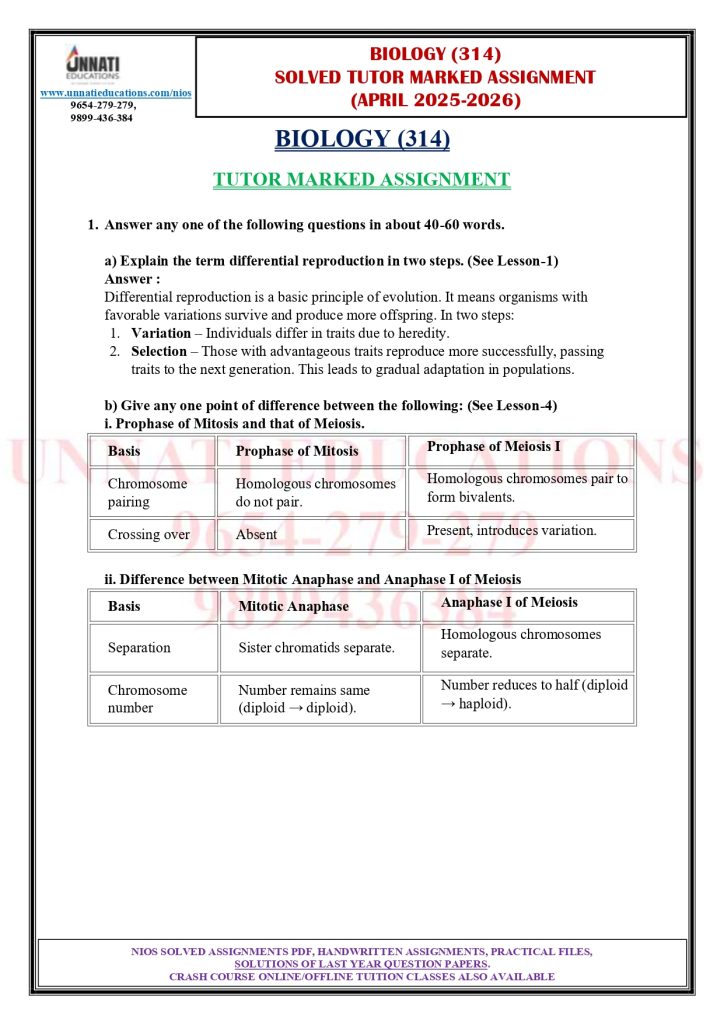
Lesson 1 concepts appear in Question 1 option (a), covering differential reproduction. This topic explains how organisms with favourable traits survive and reproduce more successfully. You need to understand the two-step process: variation in population and selection based on advantageous characteristics.
The same lesson also appears in Question 4 option (b) about nitrogen utilization in organic biomolecules. You should know how organisms synthesize amino acids, proteins, nucleotides, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll using nitrogen.
Cell Division:
Lesson 4 is heavily featured in Question 1 option (b). You must understand the differences between mitosis and meiosis, particularly comparing specific phases like prophase of mitosis versus prophase of meiosis, and mitotic anaphase versus anaphase I of meiosis. These comparisons frequently appear in both TMA and theory exams.
Human Excretory System:
Lesson 14 appears in Question 2 option (a) covering urine formation. You need to know the three sequential steps: ultrafiltration in Bowman’s capsule, selective reabsorption in tubules, and tubular secretion in the distal tubule. Understanding which part of the nephron performs each step is crucial.
Cell Biology and Osmosis:
Lesson 8 concepts appear in Question 2 option (b) about cell behaviour in isotonic and hypotonic solutions. Understanding osmosis, endosmosis, and how cells maintain stability in different concentration solutions is important.
Digestive System:
Lesson 13 covers human digestion and appears in Question 3 option (b). You should know where digestion of carbohydrates and proteins begins and completes, and what the final products are after digestion.
Biotechnology:
Lesson 23 appears in Question 3 option (a), covering DNA fingerprinting and PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). Understanding paternity testing methods and the role of Taq DNA Polymerase is important.
Muscle Physiology:
Lesson 5 appears in Question 4 option (a) about muscle contraction. The sliding filament theory explaining the interaction between actin and myosin filaments is a detailed topic requiring proper understanding.
Homeostasis:
Lesson 18 features in Question 5, covering thermoregulation and how the human body maintains constant internal temperature despite external fluctuations. This demonstrates homeostasis principles clearly.
Plant Biology:
Lesson 6 appears in Question 6 option (a), requiring the collection and description of ten plants with details about their roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, habitat, and utility. This is practical fieldwork.
Genetics:
Lesson 22 appears in Question 6 option (b) covering inheritance patterns. You need to compare inherited features between family members and understand basic genetics concepts.
Answer Approach for Different Question Types
Let me guide you through how to tackle each type of question effectively.
For 2-Mark Questions (40-60 Words):
These questions test basic understanding. Your answer should be concise yet complete. Start with a one-line definition or introduction. Then explain the concept in two to three clear points. If relevant, mention an example or application. Most importantly, count your words. Writing 35 words shows insufficient knowledge, while writing 80 words shows that you cannot follow instructions.
For example, if explaining differential reproduction, structure your answer like this: define the term in one sentence, explain step 1 about variation, explain step 2 about selection, and connect it to evolution. This covers all aspects within the word limit.
For 4-Mark Questions (100-150 Words):
These require detailed, well-organised answers. Break your answer into clear sections using headings or numbered points. Include relevant examples to support explanations. If the question asks for comparison, use a table format or a clear point-by-point structure.
For instance, when explaining muscle contraction, divide your answer into: introduction to sliding filament theory, structure of thin and thick filaments, role of calcium ions, mechanism of cross-bridge formation, and conclusion about the process. This organised approach ensures you don’t miss important points.
For 6-Mark Project Questions:
Projects require maximum effort but offer the best scoring opportunity. Choose the option requiring less fieldwork if you’re short on time. Structure your project with a clear introduction stating your objective. Present findings in organised sections with headings. Include tables or lists where appropriate. Conclude with observations or learning points.
If doing the plant collection project, create a detailed table with columns for all required information: common name, scientific name, root type, stem type, leaf arrangement, flower structure, habitat, utility, collection site, and month collected. This organised presentation earns full marks.
NIOS Class 12 Biology 314 Solved TMA 2025-26



Important Dates and Deadlines
Understanding the timeline prevents last-minute panic and ensures timely submission.
For April/May 2026 Examination Batch:
| Event | Date | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| TMA Booklet Released | August 2025 | Download from the student portal |
| Recommended Start Date | September 2025 | Begin preparing answers |
| Mid-Way Check | December 2025 | Get tutor feedback on the draft |
| Final Submission Deadline | January 31, 2026 | Submit before this date |
| Evaluation Period | February 2026 | Wait for tutor evaluation |
| Feedback Available | End February 2026 | Check marks on the portal |
| Theory Examination | April/May 2026 | Appear for the main exam |
For October/November 2026 Examination Batch:
| Event | Date | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| TMA Booklet Released | February 2026 | Download from the student portal |
| Recommended Start Date | March 2026 | Begin preparing answers |
| Mid-Way Check | June 2026 | Get tutor feedback on the draft |
| Final Submission Deadline | July 31, 2026 | Submit before this date |
| Evaluation Period | August 2026 | Wait for tutor evaluation |
| Feedback Available | End August 2026 | Check marks on the portal |
| Theory Examination | October/November 2026 | Appear for the main exam |
The deadline of January 31, 2026, for the April batch students is absolutely final. NIOS does not accept late submissions under any circumstances. Even submitting on February 1st means zero marks. Plan to submit at least five days early to avoid portal traffic issues on the deadline day.
Submission Guidelines Step by Step
Proper submission is as important as good answers. Here’s exactly what you need to do.
Preparation Phase:
Write all answers in clear, readable handwriting using a blue or black pen on clean A4 ruled sheets. Leave proper margins: 1.5 inches on the left side and 1 inch on the other sides. This makes your answers look professional and easier to evaluate.
Draw all diagrams in pencil first, then trace with a pen. Label diagrams clearly with arrows pointing exactly to the relevant parts. For tables, use a ruler to draw neat lines. Messy tables with uneven lines create poor impressions.
Create a proper cover page including your full name as per NIOS records, enrollment number, subject code 314, subject name Biology, your accredited institution name and code, and session 2025-26. Add an index page listing all questions with their page numbers.
Get your answers checked and signed by your Biology tutor at the study centre. Their signature on each answer sheet is mandatory. This verification confirms your work meets requirements.
Online Submission Process:
Log in to your NIOS Student Portal using your enrollment number and password. Navigate to the TMA submission section under examinations or assignments. Select Biology (314) and ensure you choose the correct session 2025-26.
Scan all your answer sheets as clear, high-quality PDF files. Each page must be clearly visible and readable when scanned. Poor quality scans where text is not readable create evaluation problems.
Upload the complete PDF file through the portal. The system will ask you to confirm submission. Once you confirm, you cannot edit or resubmit. Double-check everything before confirming.
After successful submission, download the receipt showing your submission date and time. Save this receipt as proof. If any technical issue arises later, this receipt proves you submitted on time.
Common Mistakes That Cost Marks
Learning from others’ mistakes helps you avoid unnecessary mark loss.
Content-Related Mistakes:
Many students significantly exceed word limits. If a question asks for 40 to 60 words and you write 95 words, evaluators may deduct marks for not following instructions. Similarly, writing only 30 words for a 40 to 60-word question shows insufficient knowledge coverage.
Choosing both options when the question clearly states “anyone” wastes your time without earning extra marks. Read instructions carefully and choose the option you’re more confident about based on your preparation.
Missing parts of multi-part questions cost significant marks. If Question 2 has parts (i) and (ii), and you answer only (i), you lose all marks for part (ii). Always check that you’ve addressed every part of each question.
Format-Related Mistakes:
Submitting typed or computer-printed TMAs leads to automatic rejection. NIOS clearly states that all answers must be handwritten. Even if your handwriting is not beautiful, as long as it’s readable, it’s acceptable. There are no exceptions to this handwritten requirement.
Using both sides of the paper can create problems. Some tutors prefer single-sided writing for easier evaluation. Check with your tutor beforehand or stick to the safer option of using one side only.
Poor quality scans where text is blurry or too light make evaluation difficult. Tutors cannot award marks for answers they cannot read properly. Use good lighting and scan settings to ensure clarity.
Submission-Related Mistakes:
Last-minute submission on deadline day is extremely risky. The NIOS portal experiences heavy traffic on deadline days, leading to slow page loading and submission failures. Many students miss deadlines this way despite having completed work.
Submitting to the wrong session or the wrong subject happens when students don’t verify their selections before uploading. Always double-check you’ve selected Biology 314 and session 2025-26 before uploading.
Not keeping backup copies of submitted work is unwise. If any technical issue arises or submission fails, having photocopies or scanned backups helps you resubmit or prove you completed the work.
How TMA Preparation Helps Theory Exams
The effort you invest in TMA preparation provides significant benefits for your theory examination.
Direct Topic Coverage:
Many topics featured in TMA questions frequently appear in theory exams. When you prepare detailed TMA answers, you’re essentially studying those topics thoroughly. For example, preparing the urine formation answer for TMA means you’ve already mastered that topic for theory exams.
Answer Writing Skills:
TMA teaches valuable answer-writing skills. You learn proper structure, how to stay within word limits, appropriate use of headings, and clear presentation. These skills directly improve theory exam performance, where presentation significantly affects marks.
Diagram Practice:
Drawing diagrams for TMA, like nephron structure, cell division stages, or muscle fibre arrangement, gives essential practice. In theory exams, well-drawn, properly labelled diagrams can earn full marks quickly and save writing time.
Concept Clarity:
Researching topics for TMA answers forces deep understanding rather than superficial memorisation. This deep clarity helps tackle different question formats in theory exams, even if the exact question style changes.
Scoring Strategy for Maximum Marks
Understanding how to maximise your TMA score requires smart planning and execution.
Target Easy Marks First:
Questions 1 and 2, with 2 marks each, are typically easiest. Choose the option you’re more confident about and answer thoroughly. These 4 marks combined should fetch you full scores with proper preparation.
Focus on Presentation Quality:
Even if the content is good, poor presentation reduces marks. Use proper headings, number your points clearly, underline important terms, and maintain neat handwriting throughout. These efforts create positive impressions on evaluators.
Master Word Limit Management:
For 40 to 60-word answers, aim for 55 to 58 words. This shows complete coverage without verbosity. For 4-mark questions requiring 100 to 150 words, write 130 to 145 words. For the 6-mark project, follow the specified requirements exactly.
Include Quality Diagrams:
Wherever relevant, include well-drawn diagrams. A properly labelled nephron diagram for urine formation or clear cell division stages can compensate for slightly less detailed text. Always use a pencil for diagrams and a pen for labels.
Get Tutor Consultation:
Before final submission, show your answers to your subject tutor if possible. They understand exactly what evaluators look for and can point out errors or suggest improvements. Their insights are invaluable.
How Unnati Education Supports Your Success
At Unnati Education, we understand that NIOS students face unique challenges, especially those balancing education with work, family, or other responsibilities.
Complete TMA Solutions:
We provide expertly prepared NIOS TMA> solutions for Biology 314 and all other subjects. Our solutions follow NIOS guidelines precisely, maintain appropriate word limits, include proper diagrams and formatting, and demonstrate the exact answer structure that earns maximum marks. You can use these as a reference to understand what evaluators expect.
Previous Year Question Papers:
Access our comprehensive collection of NIOS Previous Year Question Papers for Biology and other subjects. These papers help you understand exam patterns, identify frequently tested topics, and practice answering different question types under exam conditions.
Study Resources:
Beyond TMAs and question papers, we offer detailed study notes, topic-wise summaries, and practical file guidance through our NIOS Lab Manual support. These resources make your entire NIOS journey smoother and more successful.
Personalised Guidance:
Every student has unique challenges. Whether you’re struggling with specific Biology topics like cell division or biotechnology, need help understanding TMA requirements, or want feedback on your answer drafts before submission, our experienced Biology educators provide personalised support tailored to your needs.
Regular Updates and Reminders:
Stay informed about important NIOS notifications, including TMA deadline reminders, exam date announcements, result declarations, and any changes in submission procedures. We monitor official NIOS communications continuously and keep you updated so you never miss critical information.
Contact Information:
If you need help with your Biology 314 TMA, want access to completed assignments, require additional study materials, or have questions about NIOS examinations and procedures, reach out to us:
Phone/WhatsApp: 9654279279, 9899436384 Website: www.unnatieducations.com/nios WhatsApp Direct: wa.me/message/2I66JHXEMYLXM1 Telegram: t.me/unnatieducations Instagram: instagram.com/unnatieducation_nios
We’re committed to helping you achieve excellent results in your NIOS examinations through quality support and guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the final deadline for submitting the NIOS Class 12 Biology 314 TMA for the 2025-26 session?
The absolute final deadline is January 31, 2026, for students appearing in April-May 2026 examinations. For October-November 2026 examination candidates, the deadline is July 31, 2026. These deadlines are non-negotiable, and NIOS does not accept late submissions. Submit at least five days early to avoid last-minute portal issues and technical problems.
Can I submit typed answers, or must the TMA be handwritten?
NIOS strictly requires all TMA answers to be handwritten only. Computer-typed, printed, or photocopied submissions are rejected without evaluation, resulting in zero marks. You must write answers by hand using a blue or black pen on proper ruled sheets, scan them clearly as a PDF, and upload them through the student portal. This handwritten requirement applies universally.
How are TMA marks calculated and added to the final Biology result?
Your TMA is evaluated out of 20 marks by your subject tutor. These marks are converted to 16 marks using this formula: your TMA score divided by 20, then multiplied by 16. For example, scoring 18 out of 20 becomes 14.4 out of 16 final marks. These converted marks represent 20% weightage and combine with theory exam marks for your final result.
What happens if I answer both options when the question says choose any one?
If you answer both options when the question specifies choose any one, the evaluator will check only the first option you wrote and completely ignore the second one. This wastes your valuable time and effort without earning any extra marks. Always read question instructions carefully and choose the single option you can answer better.
Can I resubmit my TMA if I find mistakes after submission?
No, NIOS allows only one submission per subject per session. Once you upload your TMA PDF and confirm submission, you cannot change, edit, delete, or resubmit it under any circumstances. This makes careful preparation and thorough checking before submission extremely important. Always review all answers multiple times and get tutor verification before uploading.
Final Thoughts
Your NIOS Class 12 Biology 314 TMA for session 2025-26 is more than just a compulsory assignment. It’s a valuable opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of Biology concepts, earn crucial marks toward your final result, and prepare yourself thoroughly for the theory examination.
Starting early gives you sufficient time to research topics properly, prepare quality answers with proper diagrams, get tutor feedback on your work, and make necessary improvements before final submission. Don’t wait until mid-January 2026 when the deadline approaches. Begin working on your TMA in September or early October 2025 when the question booklet becomes available.
Remember that every single mark in your TMA directly impacts your final percentage. The difference between scoring 14 out of 20 versus 19 out of 20 in TMA translates to almost 4 marks difference in your final converted score. This seemingly small difference can determine whether you get admission to your desired college or miss out due to percentage requirements.
















